【JRaft源码分析02】心跳机制以及日志复制
日志复制是所有分布式共识算法最重要也是最复杂的部分,需要考虑各种各样安全性,比如机器挂了持久化没做、网络分区导致term&logindex不一致、成员变化带来两个任期相同的leader、异步网络出现日志乱序等等。
很多个细节,我边看源码边照着论文理解,一个异常判断反复推敲它的作用,想象发生的场景。这是源码级熟悉raft的好处,多多少少能身临其境,获取更多的实战校验。
后面至少还有两篇,成员变化和日志压缩。
花了点时间做张较为直观的简化流程图,红色箭头是日志复制的过程。还是挺复杂的,包括不限于Node、LogManager、Replicator、BallotBox、StateMachine之间的调用,其实还有快照,以后再讲。
本文会分为三部分讲,写请求日志落盘、日志复制、commit执行StateMachine。
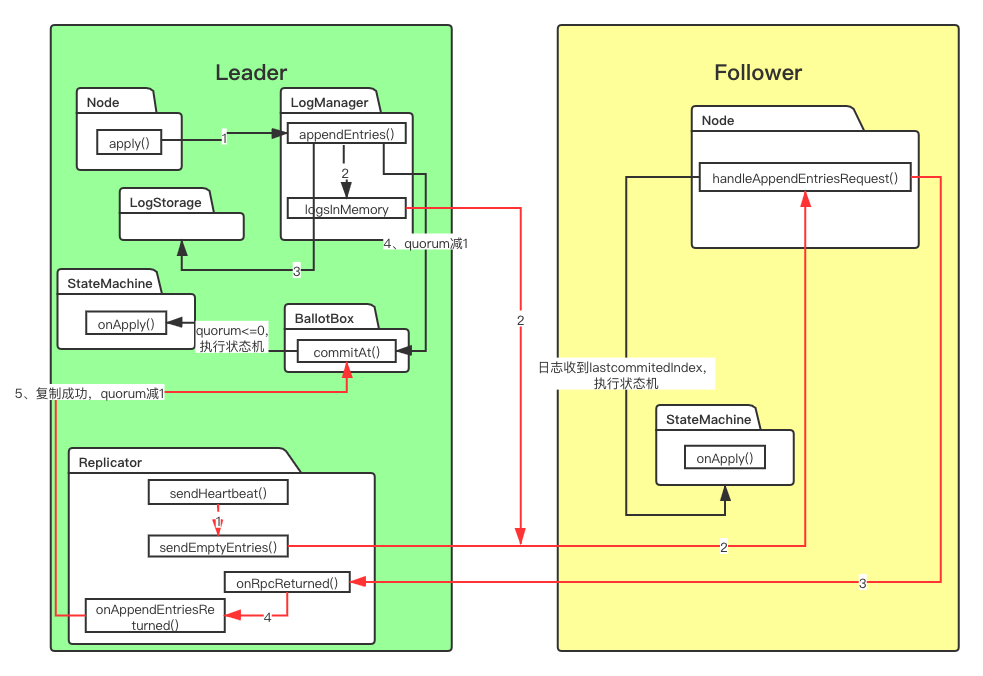
开始前,有几个全局变量需要说明一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| //下一个要发送的LogIndexId,Leader上任初始化为lastLogIndex + 1
private volatile long nextIndex;
//每次日志复制都把多个LogEntity封装进Inflight,一次发送
private Inflight rpcInFly; //这里记录最近要的一个
private final ArrayDeque<Inflight> inflights = new ArrayDeque<>();
//Raft不允许乱序日志复制,所以需要这两个字段限制某个inflight是否对应某个request和response
private int reqSeq = 0;
private int requiredNextSeq = 0; //限制顺序
|
1、什么时候写入日志的?
jraft-example里有CounterServer这个示例,IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor专门处理写入请求,可见调用了com.alipay.sofa.jraft.example.counter.CounterServiceImpl#applyOperation,然后是com.alipay.sofa.jraft.Node#apply,写入请求处理从NodeImpl.apply开始。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| public void apply(final Task task) {
if (this.shutdownLatch != null) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(task.getDone(), new Status(RaftError.ENODESHUTDOWN, "Node is shutting down."));
throw new IllegalStateException("Node is shutting down");
}
final LogEntry entry = new LogEntry();
entry.setData(task.getData()); // 封装具体操作对象,ByteBuffer
int retryTimes = 0;
try {
final EventTranslator<LogEntryAndClosure> translator = (event, sequence) -> {
event.reset();
event.done = task.getDone();
event.entry = entry;
event.expectedTerm = task.getExpectedTerm();
};
while (true) {
if (this.applyQueue.tryPublishEvent(translator)) {//JRaft在处理请求也是采用了完全异步,apply直接把任务丢到applyQueue
break; //在内部类LogEntryAndClosureHandler处理任务
} else {
retryTimes++;
if (retryTimes > MAX_APPLY_RETRY_TIMES) {
return;//applyQueue超载
}
ThreadHelper.onSpinWait();
}
}
} catch (final Exception e) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(task.getDone(), new Status(RaftError.EPERM, "Node is down."));
}
}
// class LogEntryAndClosureHandler
private final List<LogEntryAndClosure> tasks = new ArrayList<>(NodeImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch());
@Override
public void onEvent(final LogEntryAndClosure event, final long sequence, final boolean endOfBatch)
throws Exception {
//shutdownLatch balabala...
this.tasks.add(event); //32条消息以上成批处理,endOfBatch表示是否最后一个
if (this.tasks.size() >= NodeImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch() || endOfBatch) {
executeApplyingTasks(this.tasks);// 开始执行task,先生成并写入日志
this.tasks.clear();
}
}
private void executeApplyingTasks(final List<LogEntryAndClosure> tasks) {
this.writeLock.lock();
try {
final int size = tasks.size();
if (this.state != State.STATE_LEADER) {
// 这段可以自行看源码,直接调用tasks.get(i).done.run(),返回给client
return;
}
final List<LogEntry> entries = new ArrayList<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
final LogEntryAndClosure task = tasks.get(i);
if (task.expectedTerm != -1 && task.expectedTerm != this.currTerm) {
if (task.done != null) {
//Task指定expectedTerm不一致也是不行的,一般默认-1,因为用户代码是获取不到currTerm的
Utils.runClosureInThread(task.done, st);
}
continue;
}
if (!this.ballotBox.appendPendingTask(this.conf.getConf(),
this.conf.isStable() ? null : this.conf.getOldConf(), task.done)) {
//这里是追加该任务的选票箱,后面再说
continue;
}
// set task entry info before adding to list.
task.entry.getId().setTerm(this.currTerm);
task.entry.setType(EnumOutter.EntryType.ENTRY_TYPE_DATA);
entries.add(task.entry);
}//这里将操作写入日志
//落盘后调用LeaderStableClosure,给自己投一票
this.logManager.appendEntries(entries, new LeaderStableClosure(entries));
// update conf.first
checkAndSetConfiguration(true);
} finally {
this.writeLock.unlock();
}
}
|
第一篇就说到jraft很多核心逻辑都实现在EventHandler子类里,上面的处理请求和下面的日志刷盘、复制也是一样。
2、有多少个Follower就有多少个Replicator
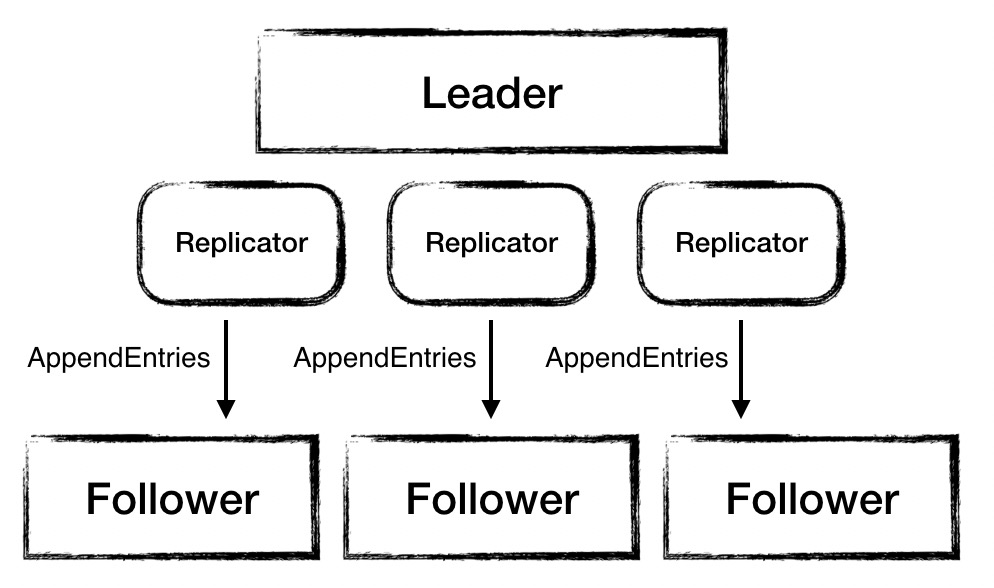
在Node赢得选举时,调用执行NodeImpl.becomeLeader()就通过replicatorGroup为每个Follower分配一个Replicator。每一个都有独立的定时器发送heartbeat、logEntity、installSnapshot,所有Replicator并发执行。
2.1 启动Replicator
start的调用可以在ReplicatorGroupImpl.addReplicator看到。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public static ThreadId start(final ReplicatorOptions opts, final RaftOptions raftOptions) {
if (opts.getLogManager() == null || opts.getBallotBox() == null || opts.getNode() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid ReplicatorOptions.");
}
final Replicator r = new Replicator(opts, raftOptions);
if (!r.rpcService.connect(opts.getPeerId().getEndpoint())) {
//建立与Follower的连接哈
return null;
}
// Register replicator metric set.
final MetricRegistry metricRegistry = opts.getNode().getNodeMetrics().getMetricRegistry();
if (metricRegistry != null) {
try {
final String replicatorMetricName = getReplicatorMetricName(opts);
if (!metricRegistry.getNames().contains(replicatorMetricName)) {
metricRegistry.register(replicatorMetricName, new ReplicatorMetricSet(opts, r));
}
} catch (final IllegalArgumentException e) {
// ignore
}
}
// Start replication
r.id = new ThreadId(r, r);//ThreadId本质上就是个锁
r.id.lock();
notifyReplicatorStatusListener(r, ReplicatorEvent.CREATED);//监听器ReplicatorStateListener.onCreated|onError|onDestroyed
r.catchUpClosure = null;
r.lastRpcSendTimestamp = Utils.monotonicMs();
r.startHeartbeatTimer(Utils.nowMs());//正式启动heartbeat timer
//这里应该是为了把becomeLeader()->this.confCtx.flush更新的配置日志同步出去,并unlock
r.sendEmptyEntries(false);
return r.id;
}
|
2.2、发送心跳包
Replicator作为一个ThreadId,需要继承内部类Thread.OnError,心跳被作为一种超时异常处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| private void startHeartbeatTimer(final long startMs) {
final long dueTime = startMs + this.options.getDynamicHeartBeatTimeoutMs();
try {
this.heartbeatTimer = this.timerManager.schedule(() -> onTimeout(this.id), dueTime - Utils.nowMs(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (final Exception e) {
onTimeout(this.id);
}
}
private static void onTimeout(final ThreadId id) {
if (id != null) {
id.setError(RaftError.ETIMEDOUT.getNumber());//调用r.onError()
} else {}//LOG
}
public void onError(final ThreadId id, final Object data, final int errorCode) {
//...
else if (errorCode == RaftError.ETIMEDOUT.getNumber()) {
id.unlock();
Utils.runInThread(() -> sendHeartbeat(id));
}//...
}
|
raft算法把心跳包也作为AppendEntries行为,也就是Follower将它视为日志消息,但可以不做处理直接返回。上面sendHeartbeat调用的是与id对应的sendEmptyEntries。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| private void sendEmptyEntries(final boolean isHeartbeat,
final RpcResponseClosure<AppendEntriesResponse> heartBeatClosure) {
final AppendEntriesRequest.Builder rb = AppendEntriesRequest.newBuilder();
if (!fillCommonFields(rb, this.nextIndex - 1, isHeartbeat)) {//填充term、groupId、lastCommittedIndex
//心跳不需要installSnapshot,暂时不管
return;
}
try {
final long monotonicSendTimeMs = Utils.monotonicMs();//最近一次发送时间
final AppendEntriesRequest request = rb.build();
if (isHeartbeat) {
this.heartbeatCounter++;
RpcResponseClosure<AppendEntriesResponse> heartbeatDone;
if (heartBeatClosure != null) {
heartbeatDone = heartBeatClosure;
} else {
heartbeatDone = new RpcResponseClosureAdapter<AppendEntriesResponse>() {
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
onHeartbeatReturned(Replicator.this.id, status, request, getResponse(), monotonicSendTimeMs);
}
};
}
this.heartbeatInFly = this.rpcService.appendEntries(this.options.getPeerId().getEndpoint(), request,
this.options.getElectionTimeoutMs() / 2, heartbeatDone);
} else {
// 发送探测请求,后面说
}
} finally {
this.id.unlock();
}
}
|
回过头看Follower的NodeImpl.handleAppendEntriesRequest是如何处理heartbeat的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| public Message handleAppendEntriesRequest(final AppendEntriesRequest request, final RpcRequestClosure done) {
boolean doUnlock = true;
final long startMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
this.writeLock.lock();
final int entriesCount = request.getEntriesCount();
try {
// 发送heartbeat的Leader已经过时了
if (request.getTerm() < this.currTerm) {
return AppendEntriesResponse.newBuilder() //
.setSuccess(false) //
.setTerm(this.currTerm) //
.build();
}
// 检查heartbeat是否来自新上任Leader,如果是,则调用stepDown并重新设置new leader
checkStepDown(request.getTerm(), serverId);//serverId.parse(request.getServerId())
if (!serverId.equals(this.leaderId)) {
//在成员变化时有可能出现两个同样任期的Leader,只需要term+1就可让两个leader下线,重新选举
stepDown(request.getTerm() + 1, false, new Status(RaftError.ELEADERCONFLICT,
"More than one leader in the same term."));
return AppendEntriesResponse.newBuilder() //
.setSuccess(false) //
.setTerm(request.getTerm() + 1) //
.build();
}
updateLastLeaderTimestamp(Utils.monotonicMs());//心跳成功更新时间
//安装或加载快照会让follower阻塞日志复制,防止快照覆盖新的commit
if (entriesCount > 0 && this.snapshotExecutor != null && this.snapshotExecutor.isInstallingSnapshot()) {
return RpcResponseFactory.newResponse(RaftError.EBUSY, "Node %s:%s is installing snapshot.",
this.groupId, this.serverId);
}
/*
* 这里证明follower日志落后于Leader
* 因为走到这里只有request.getTerm() = this.currTerm
* 所以localPrevLogTerm <= this.currTerm
* 如果prevLogIndex > lastLogIndex, 说明localPrevLogTerm=0,RocksDB未把日志刷盘,机器挂了,丢失最近一部分数据
* 如果prevLogIndex < lastLogIndex,说明localPrevLogTerm!=0 && localPrevLogTerm < prevLogTerm,日志属于过期Leader,需要保证强一致性,每行日志的term&logIndex必须一致
* 第二种情况,会在长期网络分区后出现
*/
final long prevLogIndex = request.getPrevLogIndex();
final long prevLogTerm = request.getPrevLogTerm();
final long localPrevLogTerm = this.logManager.getTerm(prevLogIndex);
if (localPrevLogTerm != prevLogTerm) {
final long lastLogIndex = this.logManager.getLastLogIndex();
return AppendEntriesResponse.newBuilder() //
.setSuccess(false) //
.setTerm(this.currTerm) //
.setLastLogIndex(lastLogIndex) //
.build();
}
if (entriesCount == 0) {
// heartbeat
final AppendEntriesResponse.Builder respBuilder = AppendEntriesResponse.newBuilder() //
.setSuccess(true) //
.setTerm(this.currTerm) //
.setLastLogIndex(this.logManager.getLastLogIndex());
doUnlock = false;
this.writeLock.unlock();
// see the comments at FollowerStableClosure#run()
this.ballotBox.setLastCommittedIndex(Math.min(request.getCommittedIndex(), prevLogIndex));
return respBuilder.build();
}
/*
* 这里有balabala,跟日志复制有关的一堆代码下面再说
*/
return null;
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.writeLock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
可以看到follower对心跳也做了一波处理。第一步,先校验对方或自己是否是合格Leader,否就让对方或自己下线;第二步,第一步正常就证明对方是一个合格的Leader以及自己是合格的Follower,那么校验双方的日志是否一致;前面一切正常了,再更新lastCommittedIndex,后面的日志同步会用到。
来看看Leader收到heartbeat回复后怎么处理.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| static void onHeartbeatReturned(final ThreadId id, final Status status, final AppendEntriesRequest request, final AppendEntriesResponse response, final long rpcSendTime) {
if (id == null) {
return;
}
final long startTimeMs = Utils.nowMs();
Replicator r;
if ((r = (Replicator) id.lock()) == null) {
return;
}
boolean doUnlock = true;
try {
StringBuilder sb = null;
//网络通讯异常
if (!status.isOk()) {
r.state = State.Probe;
notifyReplicatorStatusListener(r, ReplicatorEvent.ERROR, status);
if (++r.consecutiveErrorTimes % 10 == 0) {
}
r.startHeartbeatTimer(startTimeMs);
return;
}
r.consecutiveErrorTimes = 0;
if (response.getTerm() > r.options.getTerm()) {
final NodeImpl node = r.options.getNode();
r.notifyOnCaughtUp(RaftError.EPERM.getNumber(), true);//新节点追赶上集群,以后成员变化会说到
r.destroy();//Leader不接受任期比自己大,increaseTermTo下线
node.increaseTermTo(response.getTerm(), new Status(RaftError.EHIGHERTERMRESPONSE,
"Leader receives higher term heartbeat_response from peer:%s", r.options.getPeerId()));
return;
}
if (!response.getSuccess() && response.hasLastLogIndex()) {
doUnlock = false;
r.sendEmptyEntries(false);//日志有异常,做AppendEntries的探测请求,对应上面Follower日志校验的逻辑
r.startHeartbeatTimer(startTimeMs);
return;
}
if (rpcSendTime > r.lastRpcSendTimestamp) {
//如果Leader频繁写入,那么更新last send time多数在onAppendEntriesReturned
r.lastRpcSendTimestamp = rpcSendTime;
}
r.startHeartbeatTimer(startTimeMs);
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
id.unlock();
}
}
}
|
心跳包的代码基本就这些,heartbeat为了不重复发送选择定时而非周期Timer,直到收到响应后再次计时发送。
2.3、AppendEntries要开始了么?
日志复制可以说是绕得一批,我刚开始想当然,后来发现不是那样,很是疯狂。完全理清后,画个图比较直观。
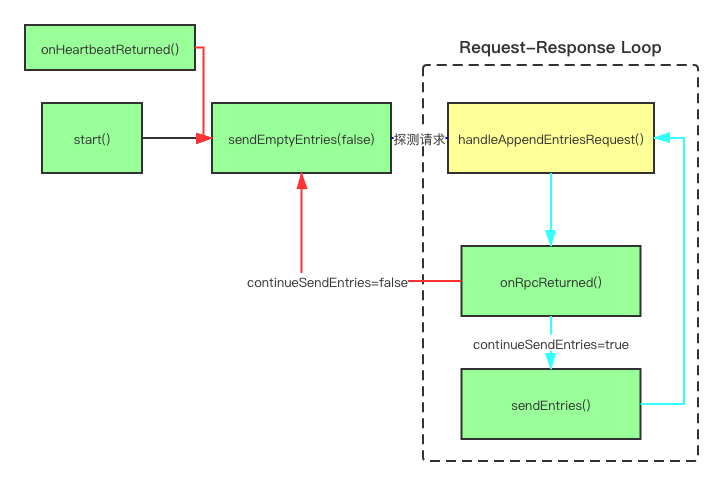
日志复制是一个请求响应自循环,最开始有start()调用sendEmptyEntries(false)做一次探测请求后正式启动。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| private void sendEmptyEntries(final boolean isHeartbeat) {
sendEmptyEntries(isHeartbeat, null);
}
private void sendEmptyEntries(final boolean isHeartbeat,
final RpcResponseClosure<AppendEntriesResponse> heartBeatClosure) {
final AppendEntriesRequest.Builder rb = AppendEntriesRequest.newBuilder();
if (!fillCommonFields(rb, this.nextIndex - 1, isHeartbeat)) {
// id is unlock in installSnapshot
return;
}
try {
final long monotonicSendTimeMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
final AppendEntriesRequest request = rb.build();
if (isHeartbeat) {
} else {
// Sending a probe request.
this.statInfo.runningState = RunningState.APPENDING_ENTRIES;
this.statInfo.firstLogIndex = this.nextIndex;
this.statInfo.lastLogIndex = this.nextIndex - 1;
this.appendEntriesCounter++;
this.state = State.Probe;
final int stateVersion = this.version;
final int seq = getAndIncrementReqSeq();//currseq=seq; seq++; return currseq;
final Future<Message> rpcFuture = this.rpcService.appendEntries(this.options.getPeerId().getEndpoint(),
request, -1, new RpcResponseClosureAdapter<AppendEntriesResponse>() {
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
onRpcReturned(Replicator.this.id, RequestType.AppendEntries, status, request,
getResponse(), seq, stateVersion, monotonicSendTimeMs);
}
});
addInflight(RequestType.AppendEntries, this.nextIndex, 0, 0, seq, rpcFuture);
}
} finally {
this.id.unlock();
}
}
|
探测请求没什么好说的,值得注意的是onHeartbeatReturned是有可能触发该探测的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
| static void onRpcReturned(final ThreadId id, final RequestType reqType, final Status status, final Message request,
final Message response, final int seq, final int stateVersion, final long rpcSendTime) {
if (id == null) {
return;
}
final long startTimeMs = Utils.nowMs();
Replicator r;
if ((r = (Replicator) id.lock()) == null) {
return;
}
if (stateVersion != r.version) {
id.unlock();
return;
}
//需要花点时间解释这个根据seq优先队列的用处
//首先要知道raft强调日志必须顺序一致的,任何并发调用onRpcReturned都可能打乱复制顺序
//假设现在this.reqSeq=3, requiredNextSeq=2,我们正在等待的reqSeq=2的响应由于种种原因还没到来
//此时某次心跳onHeartbeatReturned触发了sendEmptyEntries(false),将reqSeq改为4,也就说seq=3,而且该探测请求很快被响应且调用该方法
//后来先到的response会被先hold到pendingResponses
final PriorityQueue<RpcResponse> holdingQueue = r.pendingResponses;
holdingQueue.add(new RpcResponse(reqType, seq, status, request, response, rpcSendTime));
//某个优先级更高的请求还没被回复,需要做一次探测请求
if (holdingQueue.size() > r.raftOptions.getMaxReplicatorInflightMsgs()) {
r.resetInflights();
r.state = State.Probe;
r.sendEmptyEntries(false);
return;
}
boolean continueSendEntries = false;//是否要继续上图虚线框内的Loop
try {
int processed = 0;
while (!holdingQueue.isEmpty()) {
final RpcResponse queuedPipelinedResponse = holdingQueue.peek();//优先级最高的响应
// 根据requiredNextSeq,还有更高优先级的响应未到,仍需等待
if (queuedPipelinedResponse.seq != r.requiredNextSeq) {
if (processed > 0) {
break;//前面还有processed已经成功处理,可能会调用sendEntries(),所以break即可
} else {//优先级最高的请求会被响应,所以直接返回unlock
continueSendEntries = false;
id.unlock();
return;
}
}
holdingQueue.remove();
processed++;
final Inflight inflight = r.pollInflight();
if (inflight == null) {
// The previous in-flight requests were cleared
continue;
}
//我这里没想明白什么情况会出现queuedPipelinedResponse.seq==r.requiredNextSeq且!=inflight.seq
if (inflight.seq != queuedPipelinedResponse.seq) {
// reset state
r.resetInflights();
r.state = State.Probe;
continueSendEntries = false;
r.block(Utils.nowMs(), RaftError.EREQUEST.getNumber());
return;
}
try {
switch (queuedPipelinedResponse.requestType) {
case AppendEntries:
continueSendEntries = onAppendEntriesReturned(id, inflight, queuedPipelinedResponse.status,
(AppendEntriesRequest) queuedPipelinedResponse.request,
(AppendEntriesResponse) queuedPipelinedResponse.response, rpcSendTime, startTimeMs, r);
break;
case Snapshot:
continueSendEntries = onInstallSnapshotReturned(id, r, queuedPipelinedResponse.status,
(InstallSnapshotRequest) queuedPipelinedResponse.request,
(InstallSnapshotResponse) queuedPipelinedResponse.response);
break;
}
} finally {
if (continueSendEntries) {
// Success, increase the response sequence.
r.getAndIncrementRequiredNextSeq();
} else {
// The id is already unlocked in onAppendEntriesReturned/onInstallSnapshotReturned, we SHOULD break out.
break;
}
}
}
} finally {
if (continueSendEntries) {
// unlock in sendEntries.
r.sendEntries();//继续日志复制循环
}
}
}
|
onRpcReturned的主要功能在严格控制Leader处理请求-响应的顺序,避免乱序提交带来的数据不一致。
顺序校验后,轮到onAppendEntriesReturned了,它主要两个功能。
一个是校验Replicator.nextIndex-1与Follower.lastLogIndex是否一致,若否,则矫正;第二个,对已经复制成功的LogEntity反馈给BallotBox,quorum–。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| private static boolean onAppendEntriesReturned(final ThreadId id, final Inflight inflight, final Status status,
final AppendEntriesRequest request,
final AppendEntriesResponse response, final long rpcSendTime,
final long startTimeMs, final Replicator r) {
//这里我也没想明白满足(queuedPipelinedResponse.seq==r.requiredNextSeq && queuedPipelinedResponse.seq==inflight.seq),什么场景会出现不相等
if (inflight.startIndex != request.getPrevLogIndex() + 1) {
r.resetInflights();
r.state = State.Probe;
// unlock id in sendEmptyEntries
r.sendEmptyEntries(false);
return false;
}
if (!status.isOk()) { //follower挂了,快速失败,且阻塞一小段时间,停止日志复制
notifyReplicatorStatusListener(r, ReplicatorEvent.ERROR, status);
if (++r.consecutiveErrorTimes % 10 == 0) {}
r.resetInflights();
r.state = State.Probe;
// unlock in in block
r.block(startTimeMs, status.getCode());
return false;
}
r.consecutiveErrorTimes = 0;
if (!response.getSuccess()) {//这个也不说了
if (response.getTerm() > r.options.getTerm()) {
final NodeImpl node = r.options.getNode();
r.notifyOnCaughtUp(RaftError.EPERM.getNumber(), true);
r.destroy();
node.increaseTermTo(response.getTerm(), new Status(RaftError.EHIGHERTERMRESPONSE,
"Leader receives higher term heartbeat_response from peer:%s", r.options.getPeerId()));
return false;
}
//能走到这一步,说明任期没问题,但LogIndex有出入
if (rpcSendTime > r.lastRpcSendTimestamp) {
r.lastRpcSendTimestamp = rpcSendTime;
}
// 清除所有准备发送的LogEntity
r.resetInflights();
// 在[2.2、发送心跳包]那里handleAppendEntriesRequest有一大段注释,对应着看
if (response.getLastLogIndex() + 1 < r.nextIndex) {
// The peer contains less logs than leader
r.nextIndex = response.getLastLogIndex() + 1;
} else {
//逐一往回追溯,直到有term&LogIndex对应上的nextIndex
if (r.nextIndex > 1) {
r.nextIndex--;
} else {
// LOG.error
}
}
// dummy_id is unlock in _send_heartbeat
r.sendEmptyEntries(false);
return false;
}
// success,有可能Leader重新选举又赢了
if (response.getTerm() != r.options.getTerm()) {
r.resetInflights();
r.state = State.Probe;
id.unlock();
return false;
}
if (rpcSendTime > r.lastRpcSendTimestamp) {
r.lastRpcSendTimestamp = rpcSendTime;
}
final int entriesSize = request.getEntriesCount();
if (entriesSize > 0) { //这是一次复制请求的响应
if (r.options.getReplicatorType().isFollower()) {
r.options.getBallotBox().commitAt(r.nextIndex, r.nextIndex + entriesSize - 1, r.options.getPeerId());
}
} else {
// The request is probe request, change the state into Replicate.
r.state = State.Replicate;
}
r.nextIndex += entriesSize;//增加已经复制的偏移量
r.hasSucceeded = true;
r.notifyOnCaughtUp(RaftError.SUCCESS.getNumber(), false);
// dummy_id is unlock in _send_entries
if (r.timeoutNowIndex > 0 && r.timeoutNowIndex < r.nextIndex) {
r.sendTimeoutNow(false, false);
}
return true;//继续日志复制循环
}
|
发送日志就不说什么了,思路很清晰,整个过程如上图,是个自循环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
| void sendEntries() {
boolean doUnlock = true;
try {
long prevSendIndex = -1;
while (true) {
final long nextSendingIndex = getNextSendIndex();//获取未被发送LogIndex
if (nextSendingIndex > prevSendIndex) {
if (sendEntries(nextSendingIndex)) {
prevSendIndex = nextSendingIndex;
} else {
doUnlock = false;
break;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.id.unlock();
}
}
}
private boolean sendEntries(final long nextSendingIndex) {
final AppendEntriesRequest.Builder rb = AppendEntriesRequest.newBuilder();
if (!fillCommonFields(rb, nextSendingIndex - 1, false)) {
// unlock id in installSnapshot
installSnapshot();
return false;
}
ByteBufferCollector dataBuf = null;
final int maxEntriesSize = this.raftOptions.getMaxEntriesSize();
final RecyclableByteBufferList byteBufList = RecyclableByteBufferList.newInstance();//一个ThreadLocalList
try {
for (int i = 0; i < maxEntriesSize; i++) {
final RaftOutter.EntryMeta.Builder emb = RaftOutter.EntryMeta.newBuilder();
//(byteBufList长度超过maxBodySize || nextSendingIndex+i找不到新日志) 返回false
if (!prepareEntry(nextSendingIndex, i, emb, byteBufList)) {
break;
}
rb.addEntries(emb.build());
}
if (rb.getEntriesCount() == 0) {
//进行过快照,日志已被删除,即刻安装快照
if (nextSendingIndex < this.options.getLogManager().getFirstLogIndex()) {
installSnapshot();
return false;
}
// 没有更多日志了,等待LogManagerImpl#appendEntries的通知
waitMoreEntries(nextSendingIndex);
return false;
}
if (byteBufList.getCapacity() > 0) {
dataBuf = ByteBufferCollector.allocateByRecyclers(byteBufList.getCapacity());
for (final ByteBuffer b : byteBufList) {
dataBuf.put(b);
}
final ByteBuffer buf = dataBuf.getBuffer();
buf.flip();
rb.setData(ZeroByteStringHelper.wrap(buf));
}
} finally {
RecycleUtil.recycle(byteBufList);
}
final AppendEntriesRequest request = rb.build();
this.statInfo.runningState = RunningState.APPENDING_ENTRIES;
this.statInfo.firstLogIndex = rb.getPrevLogIndex() + 1;
this.statInfo.lastLogIndex = rb.getPrevLogIndex() + rb.getEntriesCount();
final Recyclable recyclable = dataBuf;
final int v = this.version;
final long monotonicSendTimeMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
final int seq = getAndIncrementReqSeq();
final Future<Message> rpcFuture = this.rpcService.appendEntries(this.options.getPeerId().getEndpoint(),
request, -1, new RpcResponseClosureAdapter<AppendEntriesResponse>() {
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
RecycleUtil.recycle(recyclable);
onRpcReturned(Replicator.this.id, RequestType.AppendEntries, status, request, getResponse(), seq,
v, monotonicSendTimeMs);
}
});
addInflight(RequestType.AppendEntries, nextSendingIndex, request.getEntriesCount(), request.getData().size(),
seq, rpcFuture);
return true;
}
|
最后再来看Follower怎么处理AppendEntriesRequest,如果前面校验过了的话,就开始执行下面部分代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public Message handleAppendEntriesRequest(final AppendEntriesRequest request, final RpcRequestClosure done) {
boolean doUnlock = true;
final long startMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
this.writeLock.lock();
final int entriesCount = request.getEntriesCount();
try {
//balabala,前面已经说过了
// Parse request
long index = prevLogIndex;
final List<LogEntry> entries = new ArrayList<>(entriesCount);
ByteBuffer allData = null;
if (request.hasData()) {
allData = request.getData().asReadOnlyByteBuffer();
}
final List<RaftOutter.EntryMeta> entriesList = request.getEntriesList();
for (int i = 0; i < entriesCount; i++) {
index++;//LogIndex 偏移量,即系logId = Follower.lastCommittedIndex + index
final RaftOutter.EntryMeta entry = entriesList.get(i);
final LogEntry logEntry = logEntryFromMeta(index, allData, entry);//根据entryLen偏移量截取allData
if (logEntry != null) {
// Validate checksum
// return error
entries.add(logEntry);
}
}
//落盘后调用FollowerStableClosure,给Leader一个响应,request.lastCommittedIndex大于自己,就依序执行状态机提交数据
final FollowerStableClosure closure = new FollowerStableClosure(request, AppendEntriesResponse.newBuilder()
.setTerm(this.currTerm), this, done, this.currTerm);
this.logManager.appendEntries(entries, closure);
// update configuration after _log_manager updated its memory status
checkAndSetConfiguration(true);
return null;
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.writeLock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
3、何时提交?commit到底有多折腾?
Leader和Follower提交流程大致如下,最后都会分别执行StateMachine写入client发送的数据,下面LogManager、LogStorage以后单独讲。
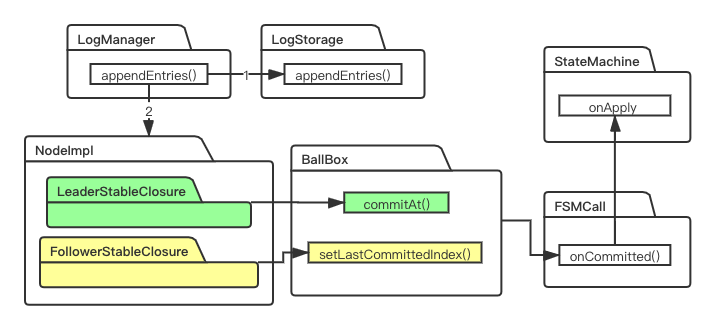
我们直接来看Leader调用的BallBox.commitAt()吧
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| public boolean commitAt(final long firstLogIndex, final long lastLogIndex, final PeerId peer) {
// TODO use lock-free algorithm here?
final long stamp = this.stampedLock.writeLock();
long lastCommittedIndex = 0;
try {//选举成功后默认lastLogIndex+1
if (this.pendingIndex == 0) {
return false;
}
if (lastLogIndex < this.pendingIndex) {
return true;
}
if (lastLogIndex >= this.pendingIndex + this.pendingMetaQueue.size()) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
final long startAt = Math.max(this.pendingIndex, firstLogIndex);
Ballot.PosHint hint = new Ballot.PosHint();
for (long logIndex = startAt; logIndex <= lastLogIndex; logIndex++) {
final Ballot bl = this.pendingMetaQueue.get((int) (logIndex - this.pendingIndex));//队列偏移量
hint = bl.grant(peer, hint);
if (bl.isGranted()) {
lastCommittedIndex = logIndex;
}
}
if (lastCommittedIndex == 0) {
return true;//没有任何提交的日志
}//这一段我没能理解
// When removing a peer off the raft group which contains even number of
// peers, the quorum would decrease by 1, e.g. 3 of 4 changes to 2 of 3. In
// this case, the log after removal may be committed before some previous
// logs, since we use the new configuration to deal the quorum of the
// removal request, we think it's safe to commit all the uncommitted
// previous logs, which is not well proved right now
this.pendingMetaQueue.removeFromFirst((int) (lastCommittedIndex - this.pendingIndex) + 1);
this.pendingIndex = lastCommittedIndex + 1;
this.lastCommittedIndex = lastCommittedIndex;
} finally {
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
this.waiter.onCommitted(lastCommittedIndex);//执行状态机
return true;
}
|
Follower就更简单了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public boolean setLastCommittedIndex(final long lastCommittedIndex) {
boolean doUnlock = true;
final long stamp = this.stampedLock.writeLock();
try {//只有leader才会初始化pendingIndex
if (this.pendingIndex != 0 || !this.pendingMetaQueue.isEmpty()) {
Requires.requireTrue(lastCommittedIndex < this.pendingIndex,
"Node changes to leader, pendingIndex=%d, param lastCommittedIndex=%d", this.pendingIndex,
lastCommittedIndex);
return false;
}
if (lastCommittedIndex < this.lastCommittedIndex) {
return false;
}
if (lastCommittedIndex > this.lastCommittedIndex) {
this.lastCommittedIndex = lastCommittedIndex;
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
doUnlock = false;
this.waiter.onCommitted(lastCommittedIndex);
}
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
}
return true;
}
|
执行状态机那一块其实没什么好讲的,属于完全正常的流程,可自行阅读源码。



